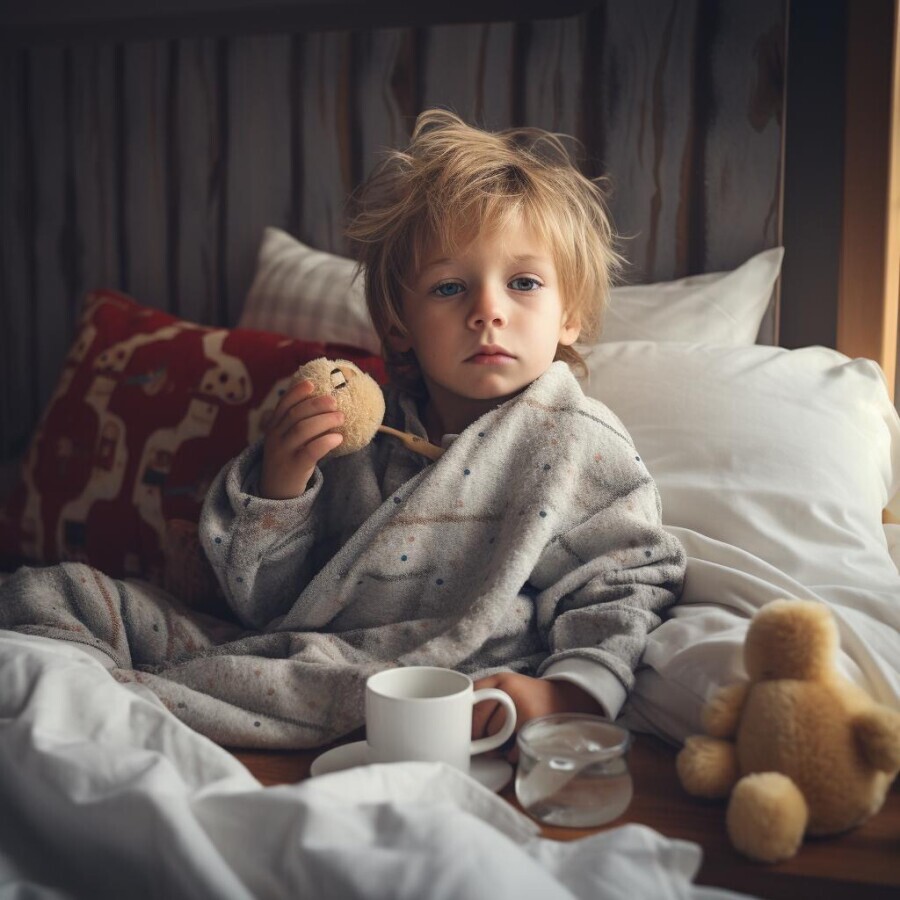
Scarlet fever, or scarlatina, is a bacterial infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, the same bacterium responsible for strep throat. Building upon our previous discussions on Scarlet Fever and Scarlet Fever in Children, this article delves into a comprehensive exploration of scarlet fever, covering its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and preventive strategies.
Causes of Scarlet Fever
Scarlet fever is primarily caused by the Group A Streptococcus bacteria. This bacterium produces a toxin that leads to the characteristic rash and other symptoms. Understanding the transmission of this bacterium is essential for preventing the spread of scarlet fever.
Common Symptoms:
- Red Rash: The hallmark symptom of scarlet fever, the rash appears like sunburn and feels rough to the touch. It often starts on the face and spreads to the trunk and limbs.
- Sore Throat: Throat inflammation is a common symptom, accompanied by difficulty swallowing.
- Fever: High fever is typical and may precede the appearance of the rash.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing scarlet fever involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. A physical examination may reveal characteristic signs, and a throat swab can confirm the presence of Group A Streptococcus bacteria. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
Treatment
Antibiotics, such as penicillin or amoxicillin, are the primary treatment for scarlet fever. Prompt administration of antibiotics not only helps in reducing symptoms but also minimizes the risk of complications. Rest and supportive care are essential for a full recovery.
Preventive Measures
Preventing scarlet fever involves a combination of personal hygiene and community awareness.
- Handwashing: Regular handwashing helps prevent the spread of the bacteria.
- Isolation: Individuals diagnosed with scarlet fever should avoid contact with others until no longer contagious.
- Vaccination: While no specific vaccine exists for scarlet fever, routine vaccinations against streptococcal infections may provide some level of protection.
Complications and When to Seek Medical Attention
Complications of scarlet fever are rare but can be severe. Watch for signs such as difficulty breathing, persistent high fever, or a worsening rash. Seek medical attention promptly if these symptoms arise.
For a detailed understanding of scarlet fever in children, refer to our earlier article on Scarlet Fever in Children. Internal linking enhances your knowledge across related topics.
Scarlet fever, though a serious infection, can be effectively managed with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, and adopting preventive measures, individuals and communities can work towards reducing the incidence and impact of scarlet fever.
Stay informed and follow our series of articles for continued insights into scarlet fever and related health topics.