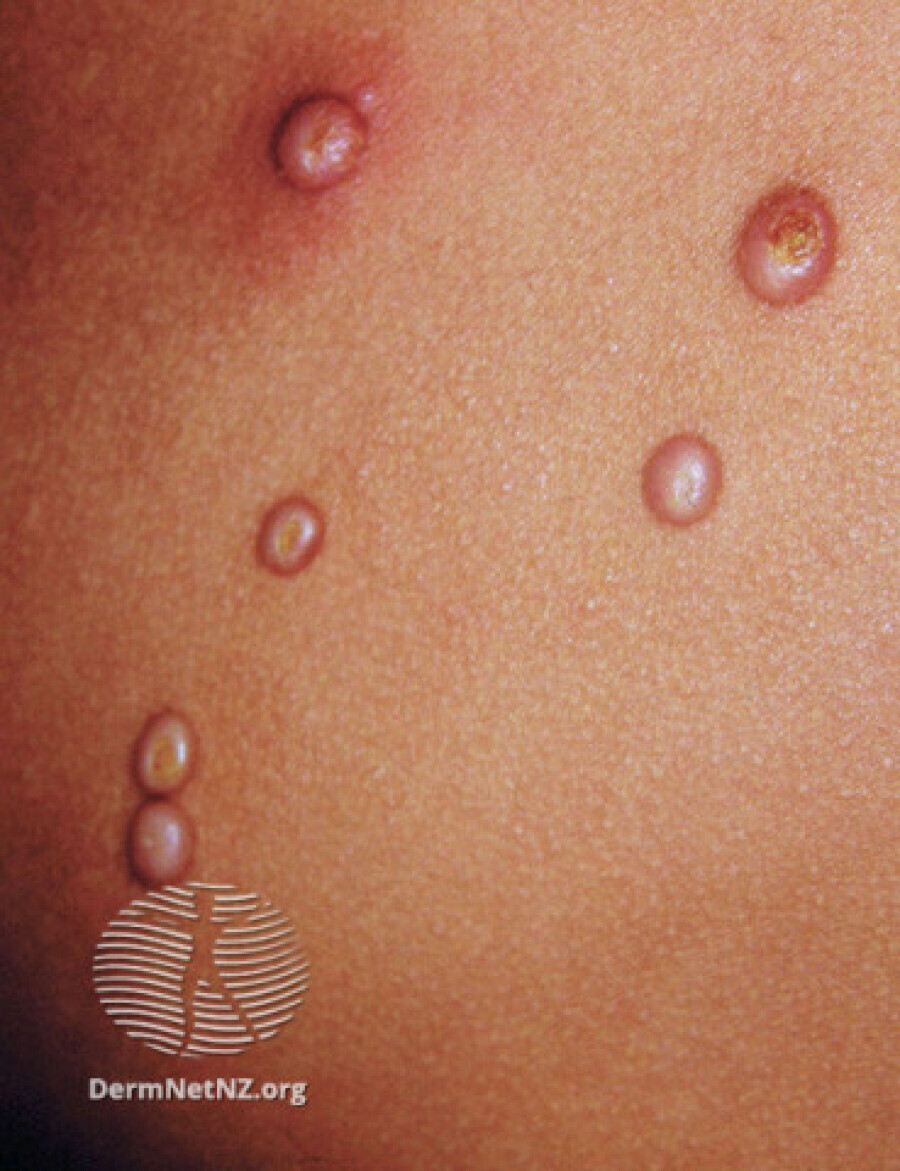
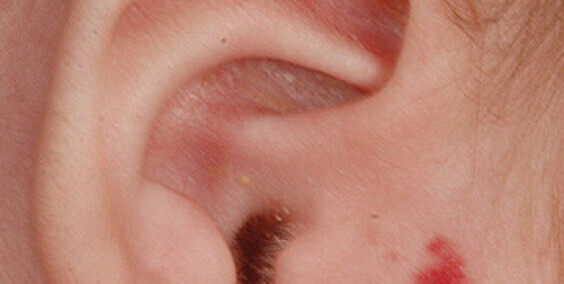
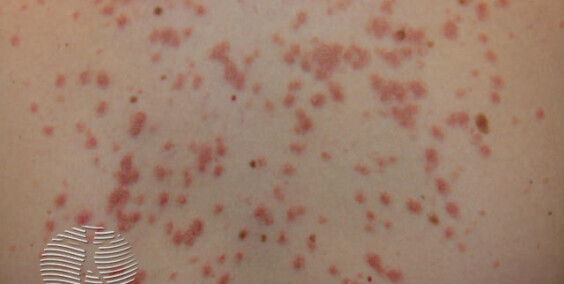
Molluscum contagiosum, also known as water warts, is a viral skin infection primarily affecting children, although it can occur in people of all ages. The causative agent is the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV), a member of the poxvirus family. The infection is characterized by the formation of small, round, pearly or flesh-colored bumps on the skin.
Symptoms
The distinctive features of molluscum contagiosum include:
- Small, raised lesions, often with a central dimple.
- Lesions are typically 2 to 5 millimeters in diameter.
- The bumps are generally painless but may become itchy, red, or swollen, particularly if irritated or scratched.
Causes
Molluscum contagiosum is highly contagious and spreads through:
- Direct skin-to-skin contact, especially in settings like schools, daycare centers, or sports activities.
- Autoinoculation, where the virus spreads to nearby skin by touching or scratching the affected area.
- Contaminated objects such as towels, toys, or surfaces.
Complications
While molluscum contagiosum is generally a benign condition, complications can include:
- Secondary bacterial infections: Scratching the lesions may introduce bacteria, leading to infections.
- Persistent lesions: In individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, the lesions may be more extensive and longer-lasting.
Prevention
To minimize the risk of molluscum contagiosum transmission:
- Avoid direct skin contact with affected individuals.
- Refrain from sharing personal items like towels, razors, or clothing.
- Practice thorough and regular handwashing, especially after touching the affected area.
Treatment
Several treatment options are available, and the choice depends on factors such as the patient's age, the number of lesions, and their location.
- Watchful waiting: In many cases, lesions resolve spontaneously over time without intervention.
- Cryotherapy: Liquid nitrogen is used to freeze and remove the lesions.
- Curettage: The lesions are scraped off using a curette, a spoon-shaped instrument.
- Topical treatments: Prescription creams containing acids (like salicylic acid) or blistering agents (like cantharidin) may be applied to the lesions.
- Laser therapy: Especially useful for larger or persistent lesions, laser therapy removes the lesions by targeting blood vessels feeding them.
Individuals with molluscum contagiosum should consult a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment recommendations. Strict adherence to preventive measures can aid in reducing the spread of the virus within communities.