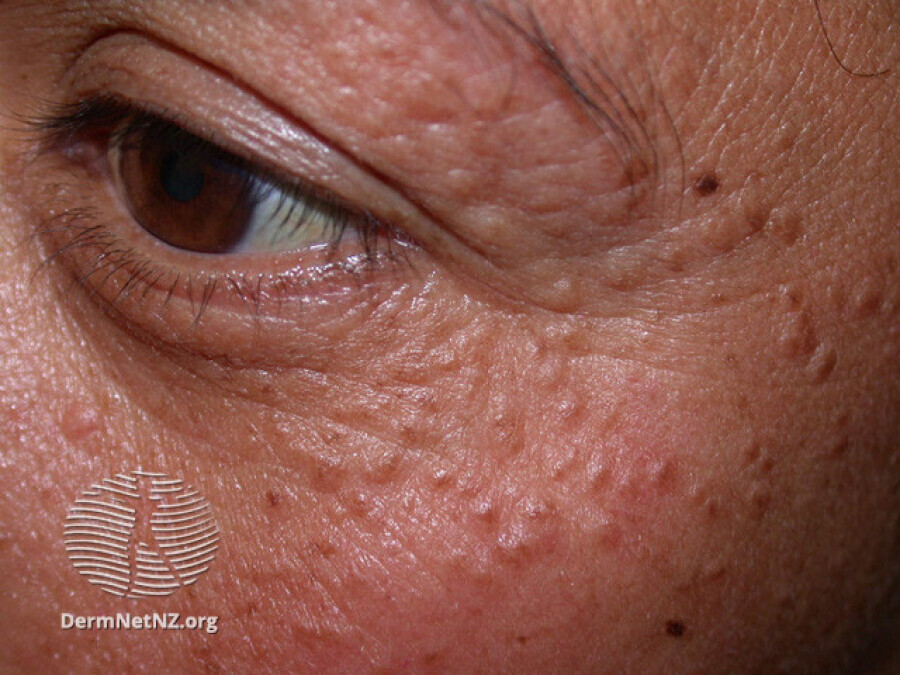
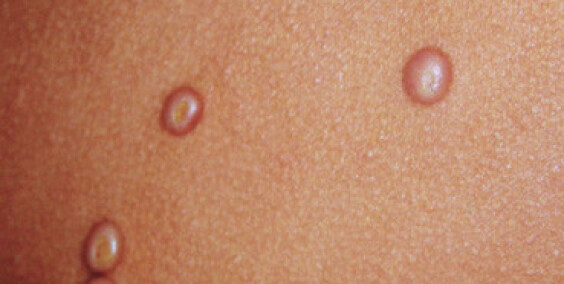
Syringomas are benign skin tumors that develop in the sweat ducts, primarily appearing as small, flesh-colored or yellowish bumps on the skin's surface. These clusters of cysts are generally harmless, yet their presence can lead to cosmetic concerns for those affected. Understanding the intricacies of syringomas is vital for accurate diagnosis and informed dermatological care.
Symptoms
- Tiny Bumps: Syringomas typically manifest as tiny, firm, round bumps on the skin, most commonly around the eyes.
- Coloration: They are often flesh-colored or yellowish, blending with the natural skin tone.
- Painless: Syringomas are generally painless but can cause itching in some cases.
Causes
The exact cause of syringomas remains unclear, but they are believed to be associated with genetic factors and the abnormal proliferation of sweat gland duct cells. They are more common in women and often emerge in adolescence or early adulthood.
Complications
While syringomas are generally benign and don't pose significant health risks, potential complications include:
- Cosmetic Concerns: Syringomas can be a source of cosmetic distress, especially when they occur on the face.
- Emotional Impact: Visible skin irregularities may impact an individual's self-esteem and confidence.
Prevention:
As the precise cause of syringomas is not well-defined, specific preventive measures are challenging. However, adopting a consistent skincare routine and seeking prompt dermatological advice for any skin irregularities can aid in early detection and management.
Treatment
- Topical Medications: Prescription creams containing retinoids or alpha hydroxy acids may help improve the appearance of syringomas.
- Laser Therapy: Certain laser treatments, such as CO2 lasers, can be employed to target and reduce the appearance of syringomas.
- Electrosurgery: High-frequency electrical currents are used to remove syringomas, particularly in smaller clusters.
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the syringomas with liquid nitrogen can be an effective method, especially for smaller lesions.
- Excision: In some cases, surgical excision may be considered for larger or persistent syringomas.
Syringomas are typically benign, their impact on appearance and emotional well-being underscores the importance of tailored dermatological care. Individuals experiencing concerns related to syringomas should consult with a dermatologist for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan. Early intervention can lead to effective management and address both the physical and emotional aspects of this skin condition.